ASK VETbytes
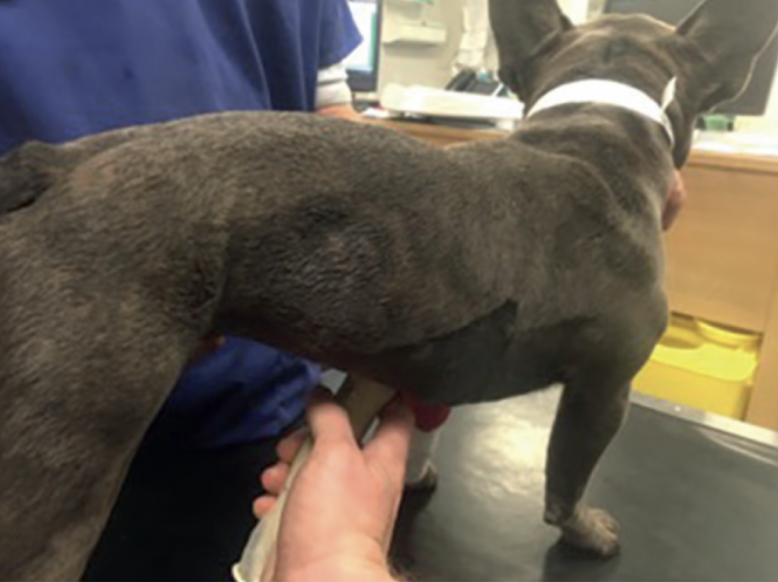
Point Of Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Buckley, C., Seitz, M., Will, R.W., et al. (2023)
Assessment of a standing position during abdominal point-of-care ultrasound on abdominal fluid score in dogs
Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care 33(5), 559-566
Abstract
QU. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the abdominal point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) techniques used to detect peritoneal effusion in dogs, as described in this study?
A. The standing approach is less reliable than the right lateral approach for detecting peritoneal effusion in dogs
B. The standing approach is more sensitive than the right lateral approach for detecting peritoneal effusion in dogs
C. The standing approach showed excellent agreement with the right lateral approach for detecting peritoneal effusion in dogs
D. The right lateral approach is significantly more accurate than the standing approach in identifying small volumes of peritoneal effusion
Click here for the answer
ANSWER
C The standing approach showed excellent agreement with the right lateral approach for detecting peritoneal effusion in dogs
MORE INFO
The study highlighted that the standing position for abdominal POCUS in dogs yielded results comparable to those obtained in the right lateral recumbency position. Both approaches showed good to excellent agreement with the gold standard full abdominal ultrasound. This makes the standing approach a viable option in clinical scenarios where lateral recumbency might not be practical or safe, such as in patients with respiratory distress or large body size. This flexibility in positioning enhances the clinical utility of POCUS in emergency settings.
SUBSCRIBE NOW
Subscribe to find out more about this article in our LATEST UPDATES section or visit our website www.vetbytes.co.uk to discover how VETbytes supports faster, better clinical decisions and improved patient care